In today’s competitive market, simply having a good product is insufficient. You need to stand out from the crowd if you want to succeed. To achieve this, a product positioning map can significantly help. It is a strategic tool that enables you to turn complex market data into a visual playbook for your brand’s success.
Effective brand positioning is not just about where you are; it’s about where you want to be in the minds and hearts of your potential customers. It’s a blend of art and science that, when executed well, can differentiate your brand from competitors, aligns with a customer need, and carve out a niche that resonates with your target audience.
Understanding where your product stands is crucial whether you’re a seasoned product manager or a marketing expert. This guide will take you through creating a product positioning map, helping you navigate to the forefront of your industry. Get ready to discover the secrets of perceptual mapping and take your brand to new heights.
Understanding Product Positioning Maps
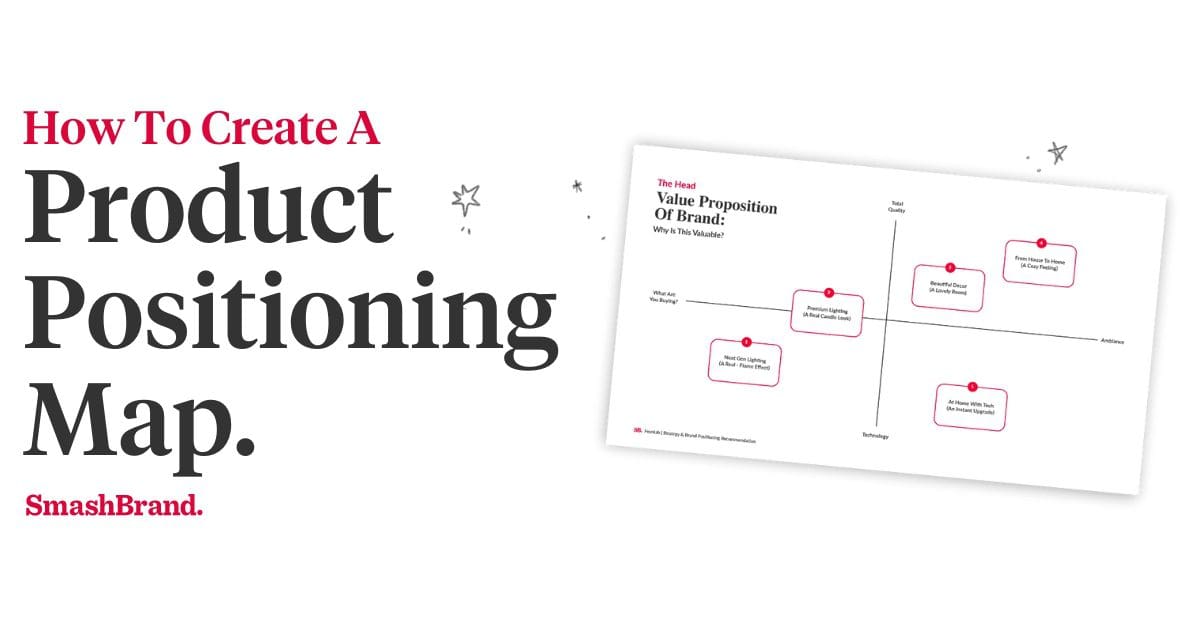
A product positioning map is a visual tool that marketers use to place their products in a two-dimensional space relative to their competitors. This space is defined by attributes important to the consumer, such as price, quality, or other relevant characteristics.
This map, known as perceptual mapping, involves research and data collection to accurately reflect how consumers view the products in a given market. The resulting perceptual map provides a graphical representation of the positioning of various products or brands in the minds of consumers, making it easier to identify how a product is perceived in different dimensions.
Importance of Product Positioning Map
Product positioning maps are crucial for several reasons. They serve as a strategic guide in marketing strategy development, helping brands identify where they stand compared to competitors and how consumers recognize them. By visualizing the competitive landscape, businesses can make informed decisions about positioning or repositioning their products.
Furthermore, a brand positioning map is not just a strategic asset; it’s also a reflection of a brand’s brand identity. It can reveal whether a brand’s identity aligns with its desired market position or if gaps must be addressed. Product positioning maps are invaluable for ensuring that a brand’s identity and market presence are coherent and effectively communicated to the target audience.
The Role of Perceptual Maps in Marketing
Perceptual maps are crucial tools in marketing as they help companies gain a deeper understanding of consumer behavior. This mind map serves as a graphical representation of how consumers perceive various products and brands within a market.
A company plots products along axes representing different attributes during a perceptual map analysis. By doing so, perceptual maps reveal the relative strengths and weaknesses of each offering from the consumer’s perspective.
This visualization uses insights from consumer perception data that consider essential factors like quality, price, service, and other attributes. Perceptual maps provide valuable insights into consumer preferences and behaviors, helping marketers understand what consumers want and how they differentiate between competing products. It allows them to see where their product stands in the competitive landscape and how they can shape their marketing strategies accordingly.
Using Perceptual Maps to Identify Market Gaps
Perceptual mapping is a strategic tool that can uncover market gaps—areas where existing products are not fully meeting consumer needs. By analyzing a perceptual map, marketers can spot opportunities for less competition and a high potential for a product to satisfy an unmet need.
For instance, market gaps exist if consumers desire a high-quality product at a moderate price but lack offerings in that space. By identifying these gaps, businesses can tailor their products and marketing efforts to meet the demands of their target market better.
This strategic use of perceptual maps can lead to increased market share. Or the repositioning of existing ones to fill voids in the market, ultimately providing consumers with choices that better align with their preferences and behaviors.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Product Positioning Map
Creating a compelling product positioning map requires careful consideration. Companies must know which attributes to plot on the axes of the map. Companies may follow these steps to create a practical positioning map to determine their positioning vs competitors.
Define Your Market and Target Audience
Identifying your target audience to create a practical product positioning map is crucial. Companies may struggle to market their products without understanding the right target audience. Therefore, businesses must conduct thorough market research to gather valuable insights. Knowing the target audience is vital because their needs and preferences should guide every decision, from product development to marketing campaigns.
Sound knowledge of the target market allows companies to tailor their product features, pricing, and messaging to specific demographics. This focused approach ensures that marketing efforts are not wasted on those unlikely to be interested in your offering, thus optimizing resources and increasing the effectiveness of your campaigns.
Identify Competing Products and Brands
During the market research, it is necessary to analyze the competing brands offering the same product or services. Companies must identify and analyze direct and indirect competitors and competing products. It involves a multi-faceted approach, including market research, consumer feedback, and competitive intelligence.
To identify your competitors, you must examine companies offering comparable products or services that meet your customer demands. It involves evaluating rival brands focusing on the same target market and audience as you are.
Next, you should perform a comprehensive analysis of your competitors’ products. Look closely at their features, benefits, pricing, distribution channels, and promotional tactics. It will help you better understand their market position, strengths, weaknesses, and customer retention strategies. By doing so, you can better craft your marketing strategy and stand out in the market.
Select Key Attributes for Comparison
Selecting the right attributes for comparison on your product positioning map is essential for it to be a valuable strategic tool. These attributes should be closely aligned with customer needs and preferences, as they will form the basis for comparing your product and the competition.
To determine the most relevant attributes for your map, start by engaging in market research to understand what factors influence your customers’ purchasing decisions. This might involve surveys, focus groups, or analyzing customer data to discern the most valued features or benefits.
Common attributes include price, quality, durability, design, user-friendliness, or innovation. However, the chosen attributes should be specific to your industry and directly related to the aspects that drive customer choice within your segment.
Incorporating these attributes into your product development process ensures that the end product meets your customers’ needs and stands out against competing offerings.
Gather Consumer Perception Data
Gathering consumer perception data is pivotal in creating an accurate product positioning map. This data reflects how consumers view your product with the key attributes you’ve identified and against competing products. Understanding customer perception is critical because it shapes the reality of your product’s market standing, regardless of your internal metrics or assumptions.
To collect this data, employ various research methods, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups, which can provide direct insights into how customers perceive your brand and products. Social media monitoring and online reviews are rich sources of brand perception data, offering unfiltered feedback on what consumers think and feel about your offerings.
This information allows you to see your product through the eyes of your customers, providing a clearer picture of your current market position and highlighting areas for improvement in product development and marketing strategies.
Plot Your Products and Competitors on the Map
Once you have identified the key attributes and gathered consumer perception data, it is time to visualize this information. Companies may visualize the data by plotting their products and competitors’ products on the positioning map. This visual representation is a powerful tool for understanding the competitive landscape and your brand position.
To create the map, choose two of the most important attributes as the axes. For example, if price and quality are the key differentiators in your market, price could be on the x-axis and quality on the y-axis. Each product or brand is then placed on the map according to and measured with a specific attribute list.
By examining a perceptual map example, you can see clusters of products with similar attributes, gaps where there may be opportunities for new products, and outliers that could represent niche players or innovative disruptors. Similarly, a brand position example can provide insights into the overall strength of a brand’s position in the market.
Brand positioning on the map should reflect the collected consumer perception data, providing a snapshot of where each brand stands in the minds of consumers. This step not only aids in understanding your current position but also helps strategize how to move your brand to a more favorable position in the future.
Analyze the Positioning Map for Strategic Insights
Analyzing the positioning map can provide valuable strategic insights that can help develop effective marketing and positioning strategies. By interpreting the map, you can determine the position of your products in the market, compare them with your competitors’ products, and identify potential areas for gaining a competitive edge.
Look for patterns that indicate market trends, such as a cluster of products in a high-quality, high-price quadrant, which might suggest consumers are willing to pay more for perceived quality. If your products are positioned outside of these clusters, you need to determine whether this is due to a unique value proposition or if it’s an area for strategic adjustment.
A strong brand positioned favorably on the map can indicate what consumers value. Conversely, understanding the positioning of more minor, emerging competitors can provide foresight into upcoming trends and shifts in consumer preferences.
Utilizing Your Product Positioning Map for Growth
Product managers are pivotal in steering products through their lifecycle, and leveraging positioning maps can be a significant asset in their product management toolkit. By using these maps, product managers can gain a visual representation of where their product stands in the competitive landscape, which is invaluable for strategic planning and decision-making.
Positioning maps help product managers align their projects with market needs and competitive dynamics. For instance, if a positioning map reveals that a product is perceived as less innovative than competitors, a product manager can use this insight to drive project initiatives to enhance the product’s innovative features.
Additionally, positioning maps can assist product managers in identifying market opportunities that may have been overlooked. By spotting these opportunities, they can initiate projects to develop new features or target underserved customer segments, thereby driving growth and ensuring that the product continues to evolve in line with market trends.
Refining Marketing Campaigns with Positioning Maps
Positioning maps offer strategic insights that can be instrumental in refining marketing campaigns across various channels, including social media and public relations. By analyzing where a product or brand sits in the competitive landscape through the lens of consumer perceptions, marketers can tailor their efforts to better resonate with their target audience.
For example, suppose a positioning map indicates that a product is perceived as cost-effective but not as high-quality as some competitors. In that case, a marketing campaign might reinforce the product’s value proposition, emphasizing its quality and affordability.
This message can be consistently communicated across social media platforms, using targeted content showcasing customer testimonials, behind-the-scenes quality control processes, or product comparisons highlighting the product’s value for money.